Optimize Injection Mold Tooling with Refined Cooling Channels & Gating
Optimize Injection Mold Tooling with Refined Cooling Channels & Gating
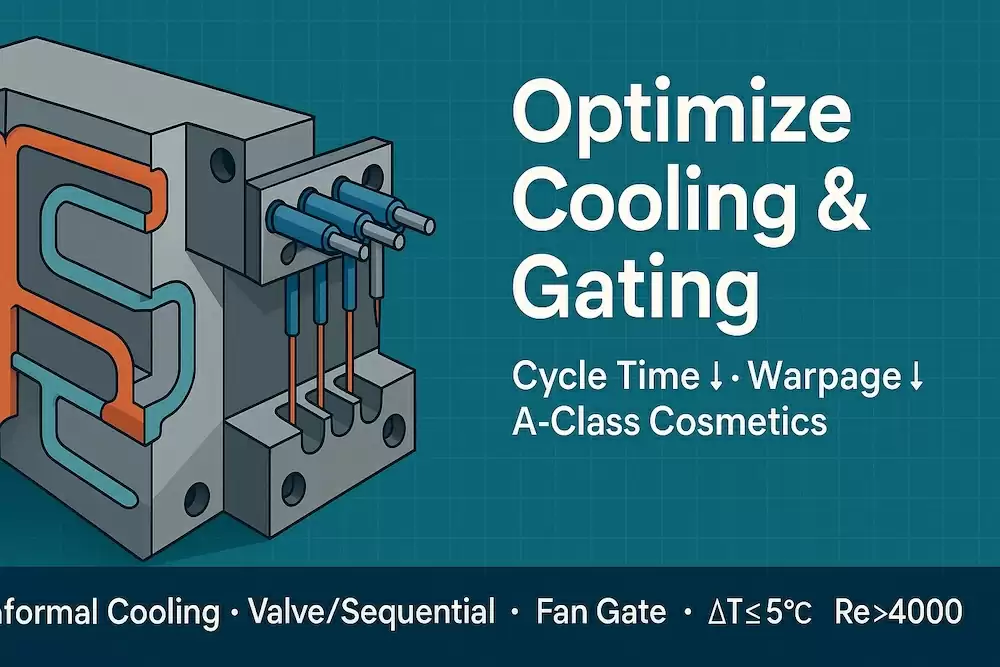
Optimize Plastic Injection Mold Tooling with Refined Cooling Channels and Gating
In injection molding, most of the cycle is cooling—and most visual/structural defects trace back to gating. Refining these two elements delivers outsized wins: shorter cycle times, lower warp, stronger knit lines, and stable CpK at critical-to-quality (CTQ) features. The TaiwanMoldMaker.com partner network co-engineers cooling and gating from Day 1, pairing simulation with scientific molding to lock a robust window.
Why Cooling & Gating Matter (In One Graphic)
-
Cooling: controls cycle time, shrink/warp, residual stress, gloss
-
Gating: controls fill balance, shear/temperature history, weld lines, gate vestige/cosmetics
Treat them as a coupled system: wrong gate → uneven fill → uneven packing → uneven cooling.
Cooling Design: Practical Rules That Move the Needle
Targets (typical starting points, adjusted per resin & geometry):
-
Channel Ø 8–12 mm for medium molds; larger plates scale up.
-
Channel depth: ~1–1.5× channel Ø from cavity surface.
-
Pitch/spacing: 2–3× channel Ø between lines.
-
Coolant ΔT loop in/out: keep within 2–5 °C across circuits.
-
Aim for turbulent flow (Reynolds > 4,000) to maximize heat transfer.
-
Balance circuits in parallel (not long serial snakes) to equalize temperature.
-
Use manifolds with similar line lengths to minimize pressure drop variations.
-
Filtration (100–200 µm) + water treatment prevents fouling and scale.
Tooling options & where they shine
| Cooling Method | Best For | Advantages | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drilled straight lines (baffles/bubblers) | General parts | Fast, economical | Add baffles near cores; avoid dead zones |
| Conformal cooling (AM/3D inserts) | Deep cores, thick/heatsinks, optics | Uniform skin temps, big cycle cuts | Great for PP/PA warpage control; plan spare inserts |
| High-conductivity inserts (Cu alloys) | Hot spots, ribs/boss clusters | Pulls heat rapidly | Coat/wear-protect as needed |
| Thermal pins/heat pipes | Localized deep cores | Passive hot-spot removal | Size for power; ensure good seating |
| Oil temp control | PC/ABS gloss, RHCM | Surface quality, reduced stress | Higher temps; seal & safety discipline |
Verification tools
-
Mold thermal simulation (CAE), IR camera on first trials, cavity thermocouples, and ΔT gauges on manifolds.
Gating Strategy: Put Flow & Cosmetics Under Your Control
Gate style selection (quick matrix)
| Gate Type | Best For | Key Benefits | Watch-outs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Edge/Tab | General parts, easy access | Simple, robust packing | Vestige, flow marks on A-side if mis-placed |
| Sub/Tunnel | Auto-de-gate small/medium parts | No secondary trim | Shear/heat on viscous resins; tool wear |
| Pin/Direct | Small round footprints | Compact vestige | Gate blush on clear/PC if too hot |
| Fan/Film | Large skins, thin walls | Low shear, weld control | More steel real estate |
| Diaphragm | Cylindrical/round parts | Central, even fill | Trim/vestige planning |
| Hot Tip | Small cosmetic gates | Reduced freeze, small vestige | Shear/gloss halos on some resins |
| Valve Gate | Multi-cavity caps, A-class parts | On/off control, no stringing | Cost/controls; pin witness management |
| Sequential Valve (Cascade) | Long flow paths/panels | Moves weld line off-view | Tight timing + sensor feedback |
Sizing and placement tips
-
Size for allowable shear (avoid splay/burn) and enough pack to control sink.
-
Keep gate land short (≈0.8–1.2 mm typical) to reduce freeze-off sensitivity.
-
Direct flow so weld lines land in non-cosmetic, low-stress zones.
-
On GF materials, align gates with load paths to manage fiber orientation/warp.
-
For clear PC/PMMA, consider hot tip + higher mold temps or RHCM to hide welds.
Rule-of-thumb reminders (for first sizing; finalize via DOE)
• Rectangular gate shear rate — keep within the resin’s window.
• Gate freeze time correlates with thickness²—thin gates freeze fast, starving pack.
Cooling × Gating: A Coupled DOE
-
Simulate fill/pack/cool to predict knit lines, pressure drop, hot spots.
-
Build with instrumentation (cavity pressure & thermocouples at critical zones).
-
DOE variables: gate temperature, open/close timing (valve), pack profile, mold temp, coolant flow/ΔT.
-
Lock golden recipe at the press: V/P transfer by cavity pressure, not just screw position.
-
SPC: monitor cycle, cavity ΔP, ΔT, and gate freeze time proxies; alarm on drift.
Typical Improvements From Refined Cooling & Gating
| KPI | Before (Conventional) | After (Refined) |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle (thin-wall ABS housing) | 28–30 s | 21–24 s |
| Warpage (150 mm PP panel) | 0.7–0.9 mm | ≤0.3–0.4 mm |
| Sink defects at bosses | Visible | Non-detectable at 50 cm |
| Cosmetic rejects | 2–4% | ≤1% |
Actuals vary by geometry, resin, and tool; these are representative.
What We Deliver (TaiwanMoldMaker.com Network)
-
48-Hour DFM Pack: gate/cooling layout, risk map, and cycle model
-
Hot runner strategy: valve/sequential with natural or engineered balance
-
Conformal-cooled inserts and high-conductivity steels where they pay back
-
Scientific molding DOE with cavity-pressure curves; recipe guardrails in MES
-
Metrology first: blue-light/CMM on CTQs, color ΔE/gloss for A-class, warpage fixtures
-
Sector quality: ISO 9001 network; IATF 16949 / ISO 13485 available at partner plants
Design Cheatsheet (Copy/Paste)
-
Walls uniform; ribs at 40–60% of wall; core heavy bosses.
-
Draft ≥1.0–1.5° textured; ≥0.5° polished; more on deep ribs.
-
Gate away from A-class; use fan/film on large skins; sequential valves for long flow.
-
Cooling circuits parallel & balanced; ΔT ≤5 °C; keep Re > 4,000.
-
Instrument at least one cavity with pressure + temp for scalable learning.
RFQ Template (Cooling & Gating Emphasis)
Subject: RFQ – Optimized Cooling & Gating (Injection Mold Tooling)
Attachments: STEP/IGES + 2D with CTQs & cosmetic map
-
Part name / revision:
-
Resin & color (grade/MFR, fills, FR/UV):
-
Cosmetic class & texture codes:
-
Priorities: (cycle ↓, warp ↓, A-class gloss, weld-line strength, etc.)
-
Preferred gate style(s) and keep-outs:
-
Cooling constraints: (press water temp/pressure, chiller capacity, oil requirement)
-
Measurement pack: (FAIR, CMM, warpage fixture, ΔE/gloss, cavity pressure curves)
-
Quantities & target dates (T0/T1/PPAP/SOP):
-
Logistics: (dual-plant, call-off, export labels)
Related Services & Quick Links
-
Custom Mold & Design Maker – DFM & CAE for gating/cooling
https://www.taiwanmoldmaker.com/product/custom-mold -
Mold Service – aluminum, hybrid, and full steel tooling
https://www.taiwanmoldmaker.com/product/mold-service -
Injection Mold – materials & processes overview
https://www.taiwanmoldmaker.com/product/injection-mold -
Molding – automated cells with valve gates & MES traceability
https://www.taiwanmoldmaker.com/product/molding -
Customer Examples – snapshots and results
https://www.taiwanmoldmaker.com/product/customer-examples
Call to Action
Want faster cycles and flatter parts without cosmetic trade-offs? Share your CAD and CTQs to receive a 48-Hour DFM & Cost Pack: gating map, cooling plan, cycle model, and qualification timeline.
Request an Instant Quote → https://www.taiwanmoldmaker.com/contact