Compare best plastics for machining versus injection molding for optimal production choices
Compare best plastics for machining versus injection molding for optimal production choices
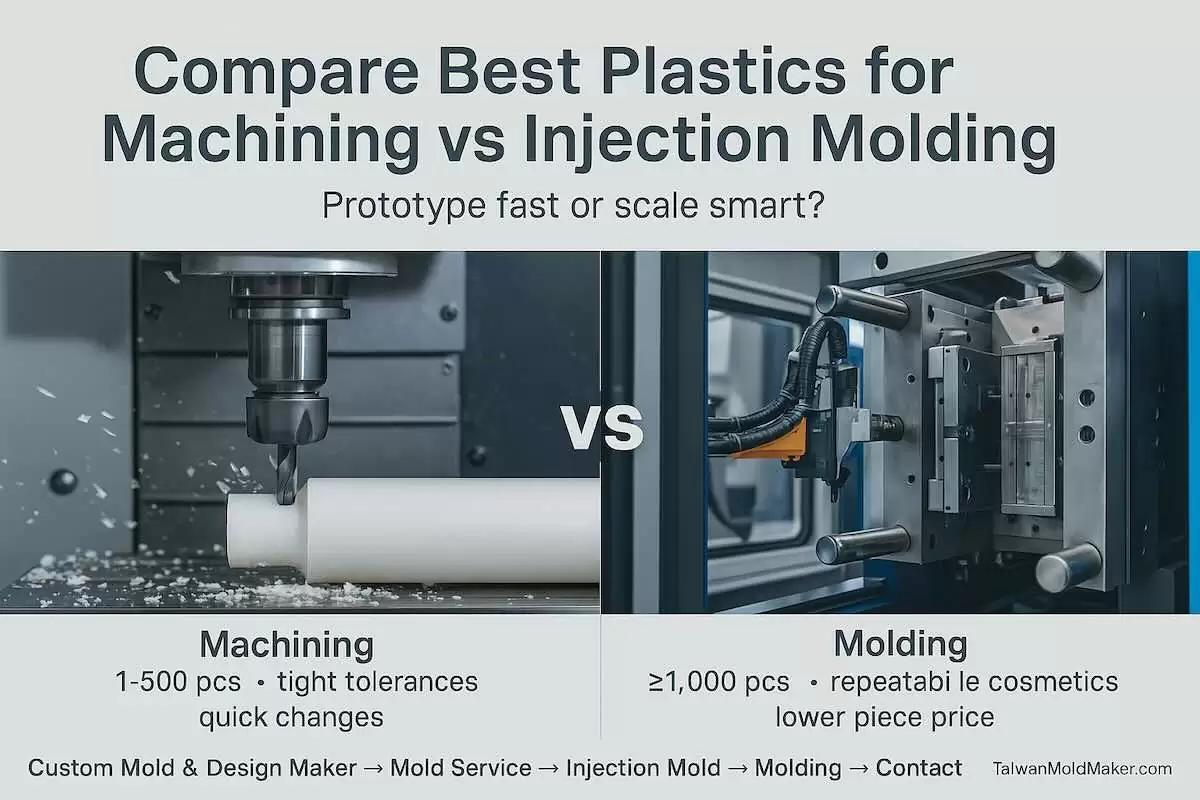
Compare Best Plastics for Machining vs Injection Molding for Optimal Production Choices
Prototype fast or scale smart? Choosing between CNC-machined plastics and injection-molded plastics starts with material behavior, part geometry, volume, and compliance. Use this guide—and the TaiwanMoldMaker.com network—to pick the right path from pilot to production.
Explore our end-to-end services:
Custom Mold & Design Maker → Mold Service → Injection Mold → Molding → Customer Examples → Contact
Quick answer: when to machine, when to mold
Choose CNC machining when…
-
Volumes are 1–500 pcs/variant (tooling ROI is weak).
-
You need tight tolerances quickly, or lots of design changes.
-
Stock shapes (rod/plate/tube) are available in your exact grade (medical, FR, UV, etc.).
-
Features are thick, localized, or deep that would make molding hard (long cooling, sink, slides).
Choose injection molding when…
-
Annual volumes are ≥1,000 pcs/SKU or multiple SKUs share a family tool.
-
You need repeatable cosmetics, low piece price, or overmold/IMD/two-shot integration.
-
Resin must be processed in production conditions (e.g., optics, controlled crystallinity).
-
You want traceability/MES and validated DOE → golden recipe for audits.
Typical break-even (guide): simple single-cavity aluminium tool justifies around 800–2,000 pcs; complex steel tools 5,000+ pcs. Your geometry and finish shift these ranges.
Plastics by process: what works best
| Polymer (common names) | Machining suitability | Injection molding suitability | Notes / where it shines |
|---|---|---|---|
| POM / Acetal (Delrin®) | Excellent | Excellent | Low friction, crisp machining; great for gears, latches, precision clips. |
| PC (Polycarbonate) | Good (stress-relieve) | Excellent | Tough, clear; optics and housings. Avoid crazing with coolants/chemicals. |
| PMMA (Acrylic) | Excellent (polish to optical) | Good | Best clarity; more brittle than PC. Stress relief improves life. |
| PA6/PA66 (Nylon) | Good (watch fuzz/moisture) | Excellent (pre-dry) | Strong; absorbs moisture → dimension control in design. |
| PA12 | Good | Excellent | Low moisture uptake; good for tubing, clips, outdoor parts. |
| PP / HDPE | Fair (burrs, soft) | Excellent | Cost-effective; great chemical resistance; cosmetics via texture. |
| ABS / PC-ABS | Good | Excellent | Stiff, paintless cosmetics with masterbatch + texture. |
| PEEK | Excellent (from rod) | Excellent (high-temp tools) | High-performance; machine for low volume, mold for scale. |
| PPSU / PSU | Good | Excellent | Repeated steam sterilization; medical trays/handles. |
| PVDF | Good | Excellent | Chemical resistance; lab/semicon fluid parts. |
| ETFE / FEP / PFA | Fair (can gum) | Excellent (high-temp) | Melt-process fluoropolymers; clean/chemical service. |
| UHMW-PE | Challenging (stringy) | Fair | Use sharp tooling; molding/secondary ops often better. |
| PTFE (Teflon®) | Excellent (from billet/sintered) | Not melt-moldable | Consider insert parts, compression molding, or coatings. |
| COC / COP | Fair (optics risky) | Excellent | Microfluidics/optics; prefer molding for stability. |
| TPE / TPU | Poor (gummy) | Excellent (esp. overmold) | Best for seals, grips; design mechanical locks. |
Always verify the grade datasheet for FR (UL 94), medical/food contact, UV, and sterilization.
Tolerances, surface, and structure
-
Machining: ±0.05 mm (or better) is routine with good fixturing; surfaces can be polished, but anisotropy is minimal vs molding. Heat from cutting can induce stress—anneal/stress-relieve PC/PMMA/PEEK when critical.
-
Molding: Tight CTQs are achieved via scientific molding (V/P by pressure, cavity sensors, gate-freeze). Expect mold-induced anisotropy/warp—handled in DFM (flow/cool/warp) and DOE. Textures require draft 1.5–3.0°.
Cost & lead-time reality check
| Factor | CNC Machining | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| NRE (tooling) | $0–Low | Medium–High (Al → Steel) |
| Piece price | High | Low at volume |
| Lead time to FA | 1–7 days | 7–28 days to T0/T1 (tool build) |
| Design changes | Easy (modify toolpaths) | Costly (steel rework/new inserts) |
| Cosmetics | Tool-marks unless finished; paint/coating optional | Repeatable textures, IML/IMD, two-shot, overmold |
| Automation & data | Limited unless fixtured | MES/vision/traceability native |
Decision guide (use this with your team)
-
Annual demand by SKU
-
< 800 pcs → Machine (or bridge tool if molding data is needed).
-
800–5,000 pcs → Al/MUD single cavity; compare to machining.
-
5,000 pcs → Steel tool; consider multi-cavity/family.
-
Geometry & finish
-
Thick/heavy mass, deep pockets → Machine first.
-
Paintless texture, tight knit-line control, overmold → Mold.
-
Material constraints
-
PTFE/UHMW-PE optics? → Machine.
-
COC/COP optics, TPE overmold, high-temp fluoropolymers → Mold.
-
Compliance & audits
-
Need DOE, CpK, genealogy → Mold with MES.
-
One-off fixtures, jigs, service parts → Machine.
Hybrid strategy (fast pilot → scalable production)
-
Phase 1: CNC from the production resin (or nearest equivalent) to validate fit/function/tests.
-
Phase 2: Bridge tool (aluminium/MUD) for T0/T1 data, cosmetic maps, ΔE/gloss, leak/functional tests.
-
Phase 3: Copy-cavity steel for ramp once demand lands; retain machining for fixtures and ECO buffers.
DFM tips to keep either path on schedule
-
Uniform walls (1.5–3.0 mm) for molding; add ribs instead of mass.
-
Gates & parting lines located away from cosmetics; plan ejector patterns.
-
Boss standards & inserts (heat-set/ultrasonic) to avoid thread failures.
-
Post-machining of molded parts for µ-level bores/threads when needed.
-
Stress relief of machined PC/PMMA/PEEK before critical inspection.
RFQ checklists (copy/paste)
For CNC machining
-
CAD (STEP/IGES) + 2D with GD&T and tolerances.
-
Material + grade (compliance needs), stock form/size, color.
-
Finish (polish/paint/anodize/coating), quantity by lot, inspection plan.
For injection molding
-
Target T1/SOP dates and milestones (DFM, T0, T1).
-
Material options & compliance (UL/food/medical/UV/FR).
-
Cavitation plan (single → family/multi), slides/hand-loads, overmold/IMD/two-shot if any.
-
Quality package (FAIR, CMM/scan, CpK targets), cosmetic map & texture codes.
-
Data/traceability (MES access: OEE, CpK, scrap, kWh/kg, genealogy).
-
Logistics (FA courier, export packing, Incoterms).
Send your package here → Contact
Why TaiwanMoldMaker.com
-
One accountable owner from DFM to SOP across CNC + molding.
-
Bridge-to-scale strategy: machined pilots → aluminium/MUD → copy-cavity steel.
-
Audit-ready data (vision + MES) to accelerate approvals.
Start here:
Custom Mold & Design Maker → Mold Service → Injection Mold → Molding → Customer Examples → Contact