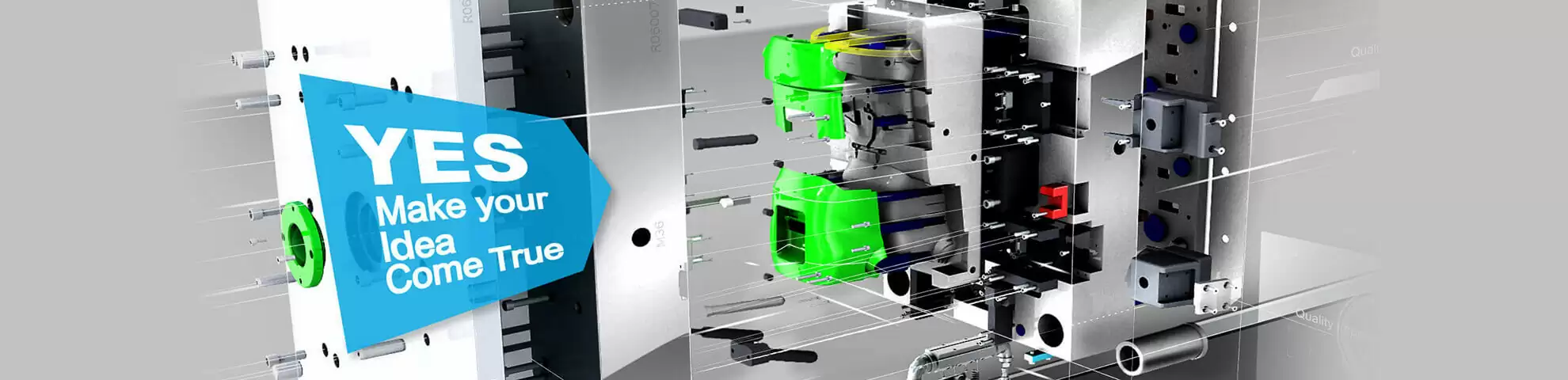
Implement gas injection molding to minimize part weight and cycle times
Implement gas injection molding to minimize part weight and cycle times

Implement Gas Injection Molding to Minimize Part Weight and Cycle Times
Hollow-core structures • Reduced material usage • Faster cooling and higher productivity
As plastic components become larger, thicker, and more structural, conventional injection molding often leads to excessive part weight, long cooling times, sink marks, and high material costs. To overcome these limitations, many manufacturers are choosing to implement gas injection molding (GIM) as a proven way to optimize both part performance and production efficiency.
At TaiwanMoldMaker.com, we help customers apply gas-assisted injection molding to reduce weight, shorten cycle times, and improve cosmetic quality—while maintaining strength and dimensional stability.
What is gas injection molding?
Gas injection molding is an advanced molding process in which nitrogen gas is injected into the molten plastic inside the mold after initial filling. The gas displaces plastic from thicker sections, creating hollow internal channels while pushing the melt uniformly against the cavity walls.
This process allows manufacturers to produce parts that appear solid externally but are lighter, stronger, and faster to mold than conventional solid parts.
Learn how this integrates with our tooling approach under Injection Mold.
Key benefits of gas injection molding
1. Minimized part weight
By hollowing out thick sections:
-
Material usage is significantly reduced
-
Overall part weight decreases without sacrificing stiffness
-
Handling, assembly, and shipping become more efficient
This is especially valuable for large housings, frames, handles, and structural components.
2. Shorter cycle times
Thick-wall parts typically drive long cooling times. Gas injection molding:
-
Removes heavy internal mass
-
Accelerates cooling and solidification
-
Reduces overall cycle time per shot
Shorter cycles directly translate to higher output and lower cost per part in volume production.
3. Improved surface quality
Gas pressure packs material evenly against mold surfaces, helping to:
-
Eliminate sink marks in thick areas
-
Reduce warpage and residual stress
-
Improve cosmetic appearance on visible parts
This makes gas-assisted molding suitable for consumer-facing and cosmetic housings.
4. Better strength-to-weight performance
Although less material is used, gas-assisted parts often deliver:
-
Higher stiffness-to-weight ratios
-
More uniform load distribution
-
Reduced internal stress compared to solid molded parts
This is ideal for applications requiring lightweight yet rigid structures.
Typical applications for gas injection molding
Gas injection molding is commonly applied to:
-
Large plastic housings and enclosures
-
Handles, grips, and frames
-
Furniture and appliance components
-
Automotive interior and structural parts
-
Industrial components with thick ribs or bosses
If your part currently suffers from sink marks or long cycles, it may be a strong candidate for gas-assisted molding.
Design considerations for successful gas injection molding
To fully benefit from gas injection molding, parts must be designed specifically for the process:
-
Gas channel planning
Internal pathways must guide gas penetration in a controlled and repeatable manner. -
Wall thickness strategy
Thick sections are ideal candidates for hollowing, while outer walls remain uniform. -
Gate and gas pin placement
Proper positioning ensures predictable gas flow and consistent hollow geometry. -
Material compatibility
Common resins include ABS, PC-ABS, PP, PA, and other thermoplastics suitable for gas assistance.
These factors are evaluated early during Custom Mold & Design Maker and Mold Service reviews.
Tooling requirements for gas injection molding
Gas-assisted molding requires purpose-built tooling, not simple modifications:
-
Integrated gas pins or gas channels
-
Mold sealing designed to withstand internal gas pressure
-
Precise timing control between melt injection and gas injection
-
Optimized venting to prevent gas blow-through
Our tooling engineers manage these requirements through Injection Mold services to ensure stable and repeatable production.
Process control and validation
Consistent gas injection molding depends on disciplined process control, including:
-
Synchronization of melt injection, gas injection, and holding stages
-
Monitoring of gas pressure and penetration length
-
Scientific molding methods to define a robust process window
-
First Article Inspection (FAI) and dimensional validation
Once validated, parameters are transferred into stable production through Molding operations.
Typical project timeline
A representative gas injection molding program may follow this structure:
-
Day 0–2: DFM review and gas-assist feasibility study
-
Day 3–10: Tool design and build with gas integration
-
Day 11–13: T0 trial focusing on gas penetration and surface quality
-
Day 14–15: T1 samples with dimensional and cosmetic approval
-
Day 16+: Production ramp with optimized cycle time
Actual timing depends on part size, geometry complexity, and validation scope.
RFQ checklist for gas injection molding
To evaluate whether gas injection molding is suitable for your application, please prepare:
-
3D CAD (STEP/IGES) and 2D drawings
-
Target weight reduction or cycle-time improvement goals
-
Preferred material or performance requirements
-
Cosmetic expectations (visible vs. non-visible surfaces)
-
Annual volume forecast and production plan
-
Structural or load-bearing requirements
Submit your project details here:
Contact
Why implement gas injection molding with TaiwanMoldMaker.com
-
Proven experience with gas-assisted injection molding processes
-
Engineering-led DFM and tooling development
-
Purpose-built molds designed for weight and cycle-time optimization
-
Reliable transition from pilot trials to full production
-
Transparent project management and quality control
If you are looking to implement gas injection molding to minimize part weight and cycle times, TaiwanMoldMaker.com provides the technical expertise and manufacturing discipline needed to deliver measurable cost and performance advantages.
Start here:
Custom Mold & Design Maker →
Injection Mold →
Molding →
Contact